자료구조 - 리스트
리스트
리스트(List)란 선형자료구조로써 데이터를 논리적 순서대로 저장하는 자료구조이며, 구현방법에 따라 두가지로 나뉩니다.
- 순차 리스트 (Sequential List)
- 연결 리스트 (Linked List)
선형자료와 비선형자료 구조는 다음과 같은 특성을 가지고 있습니다.
-
선형자료 구조 : 데이터 뒤에 하나의 데이터가 있는 형태로, 자료가 순차적으로 저장되어 있는 자료구조 (스택/큐/리스트)
-
비선형자료 구조 : 데이터 뒤에 여러개의 데이터가 있는 형태로, 자료가 계층적으로 저장되어 있는 자료구조(트리/해시/그래프)
순차리스트(배열)
순차리스트는 데이터를 논리적 순서대로 물리적 공간(메모리 주소)에 연속하여 저장하는 자료구조입니다. 이러한 특성과 함께, 순차리스트에서 데이터는 아래처럼 다루어집니다.
• 데이터 저장
앞에서부터 순서대로 저장됩니다. (메모리 물리적 위치도 순서대로)
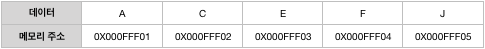
• 데이터 삽입
데이터가 삽입되면 뒤쪽 데이터가 밀립니다.
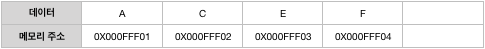
↓

• 데이터 삭제
데이터가 삭제되면 뒤쪽 데이터가 빈공간을 채웁니다.

↓
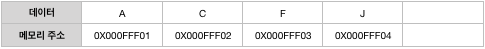
순차 리스트는 메모리가 정적으로 할당됩니다. 따라서 할당된 저장공간을 바꿀 수 없기 때문에, 저장공간을 넘는 데이터를 저장 못하는 등 몇몇 문제점이 있습니다. 이러한 한계점은, 메모리를 동적으로 구성하여 데이터를 저장하는(동적자료구조) 연결리스트로 해결될 수 있습니다.
• 빅오
순차리스트의 추가/삭제/탐색/삽입의 빅오에 대해 알아보겠습니다. 아래는 순차리스트를 보여주며, 어떤 값이 들어있는지 모릅니다.

이러한 순차리스트에 데이터를 추가할려면 어떻게 해야할까요? 자료크기에 상관없이 끝에 데이터만 추가하면 되기때문에 빅오는 O(1)입니다.

데이터 삭제 또한 추가와 동일하게, 끝의 데이터를 삭제하면 되며, 빅오는 O(1)이 됩니다.

데이터를 찾을 때, 처음부터 탐색해야 되기 때문에 빅오는 O(n)이 됩니다.

데이터를 특정 위치에 삽입을 하기 위해서, 우선 특정 위치를 탐색하고 삽입해야 되기 때문에 빅오는 O(n)이 됩니다.

연결리스트
연결리스트는 선형구조로 데이터와 다음 노드 위치(메모리 주소)를 담고 있는 노드들이 연결되어 있는 자료구조입니다. 이러한 특성과 함께 다음 노드위치만 가리키면 되기 때문에 메모리를 동적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
Linked List Data Structure - GeeksforGeeks
VisuAlgo - Linked List (Single, Doubly), Stack, Queue, Deque
노드가 어떤 노드를 가리키고 있는지에 따라, 1)단일 연결리스트 2)이중 연결리스트 3)환형 연결리스트로 구분됩니다.
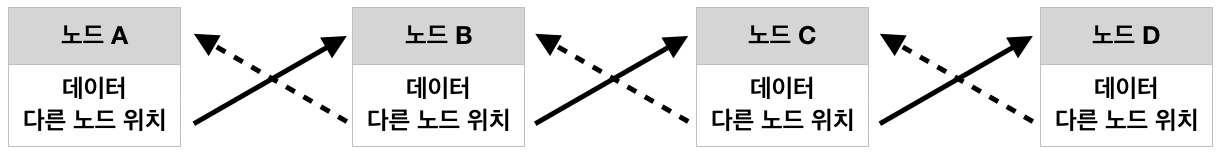
• 단일 연결리스트 (Single Linked List)
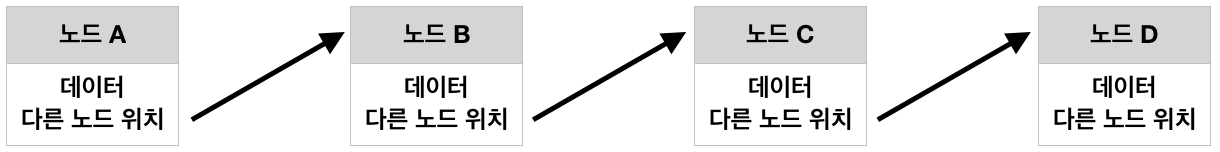
• 이중 연결리스트 (Double Linked List)
• 환형 연결리스트 (Circular Linked List)
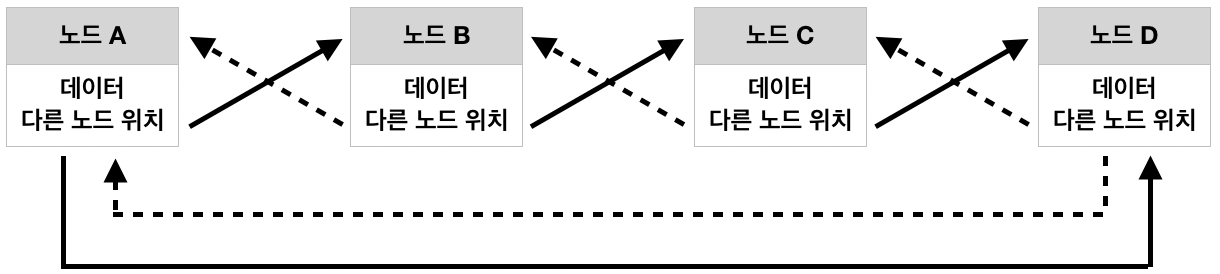
이처럼 요소끼리 서로의 메모리 주소를 참조하기 때문에, 데이터 수정(삽입/삭제 등)이 있을지라도 메모리 할당을 동적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
• 예시
- The history section of web browsers
- Line of people standing for food
• 빅오
연결리스트의 추가/삽입/삭제/탐색의 빅오는 순차리스트와 동일합니다.
• 연결 리스트 코드
- 연결 리스트는 head, tail 속성과 add, remove, contain, insert + (reverse, cycle) 메소드를 가집니다.
- 노드는 value, next 속성을 가지며, next는 다음 노드를 가리킵니다.
function linkedList () {
const linkedlist = {};
linkedList.head = null;
linkedList.tail = null;
linkedList.addHead = function (value) {
const node = Node(value);
if (!linkedList.head) {
linkedList.head = node;
linkedList.tail = node;
return;
}
node.next = linkedList.head;
linkedList.head = node;
}
linkedList.addTail = function (value) {
const node = Node(value);
if (!linkedList.head) {
linkedList.head = node;
linkedList.tail = node;
return;
}
linkedList.tail.next = node;
linkedList.tail = node;
}
linkedList.removeHead = function (value) {
linkedList.head = linkedList.head.next;
}
linkedList.contain = function (value) {
let currentNode = linkedList.head;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
return true;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return false;
}
linkedList.remove = function (value) {
let currentNode = linkedList.head;
let previousNode;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
return;
}
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
linkedList.insert = function (target, value) {
const node = Node(value);
let currentNode = linkedList.head;
let previousNode;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === target) {
node.next = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next = node;
return;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
}
linkedList.reverse = function () {
let currentNode = linkedList.head;
let previousNode = null;
linkedList.head = linkedList.tail;
linkedList.tail = currentNode;
while (currentNode) {
const temp = currentNode.next;
currentNode.next = previousNode;
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = temp;
}
}
return linkedList;
}
function Node (value) {
const node = {};
node.value = value;
node.next = null;
return node;
}
이중 연결리스트 코드
- 이중 연결 리스트는 head, tail 속성과 add, remove, contain, insert + (reverse, cycle) 메소드를 가집니다. - 노드는 value, next 속성을 가지며, next는 다음 노드를 가리킵니다.
function LinkedList () {
const linkedList = {};
linkedList.head = null;
linkedList.tail = null;
linkedList.addTail = function () {};
linkedList.removeHead = function () {};
linkedList.remove = function () {};
linkedList.insert = function () {};
linkedList.reverse = function () {};
linkedList.insert = function () {}
return linkedList;
function Node () {
const node = {};
node.value = null;
node.next = null;
}